Blockchain technology has been a matter of discussion for quite a while now as it is becoming more prevalent in industries of almost every sector. This widespread use of blockchain is due to its extraordinary features that have the potential to resolve several complications faced by industries during their operations. In this blog post, we will review some industries that widely use blockchain technology. We will also analyze what good blockchain does to these industries and how blockchain systems are better than conventional methodologies.

Healthcare
Blockchain has been used widely in almost every aspect of the healthcare industry. The reason is that blockchain has the power to solve many issues that have afflicted the healthcare industry’s history.
One of the health sector’s major issues is securing personal and sensitive medical data and records. 692 large data breaches in the healthcare sector were recorded between July 2021 and June 2022. The miscreants stole payment information as well as health and genomic records. For this reason, many hospitals have shifted their record systems to the blockchain.
Blockchain records are decentralized, transparent, and secured by cryptography. So no hacker can expose the identity of a specific record unless provided with a specific address. Thus the odds of a data breach are highly reduced.
Healthcare is a resource-intensive industry because of high hospital costs and inefficient practices. As of 2021, the US has spent almost 20 percent on healthcare. Blockchain has offered various refinements that can make healthcare functions more cost-effective.
Blockchain reduces the need for several middlemen and authorities. This cuts down costs charged by these agencies and reduces human errors. Blockchain-based records maintain patients’ privacy as their data can be shared strictly with authorized personnel. Blockchain is used in the supply chain to track medicine and drugs, preventing their illegal supply and canceling counterfeit drugs. It can also be used to monitor waste emissions.
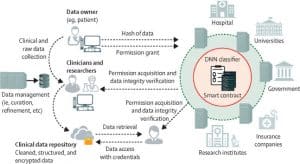
Figure 1: Blockchain-based health-care data management system between multiple stakeholders (nodes) within a health-care ecosystem (Ng, Wei Yan et al)
Finance and Banking
Finance is another area where blockchain is finding new applications exponentially. Various multinational companies are continuously adopting cryptocurrencies for financial transactions.
Blockchain provides more security and transparency than conventional methods. Blockchain is a shared ledger that is visible to everyone. This ensures transparency among the network members. Every information added to the ledger is modified by a maximum number of participants. Also, one can update or modify records without the consensus of the majority of the participants. This ensures security, clarity, and prevention of fraud.
Distributed ledger also negates the compulsion of preparing records, reconciliations, and other exhausting paperwork. It also helps in faster identification of potential risks or mistakes.
Smart Contracts, an application of blockchain, are stored on the blockchain and are executed automatically when a decided set of conditions is met. The automation provided by blockchain helps reduce costs and time requirements. Banking systems also use blockchain for client onboarding, anti-money laundering, and fraud protection.
Decentralized finance(DeFi) refers to shifting from traditional, centralized financial systems to peer-to-peer finance empowered by blockchain. DeFi offers a wide range of financial services like lending, borrowing, and stablecoins and has become the most prominent sector in the blockchain space, with over $13 billion worth of value locked in Ethereum smart contracts.
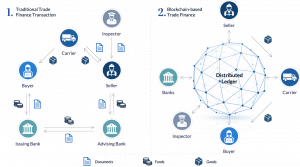
Figure 2: Traditional Trade Finance Transaction vs Blockchain-based Trade Finance.
Supply Chain Management
Blockchain is improving supply chain management in several ways. Smart contracts are one of the applications of blockchain in SCM. Smart contracts reduce the need for intermediaries and increase supply chain management’s automation, transparency, security, and efficiency.
Blockchain technology is used to track and trace products throughout their life cycle. This reduces the odds of fraud and corruption. The “trustless” nature of blockchain helps resolve trust issues between stakeholders in the supply chain.
Blockchain can also be used to track the conditions of the products, like temperature. If a medicine or food product is shipped at a particular temperature, it can be monitored throughout its journey to ensure the consumer receives a safe and quality product.
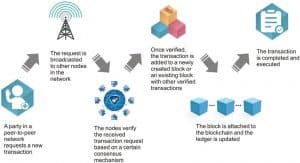
Figure 3: Blockchain-based supply chain management
Government
The record-keeping power of blockchain enables governments to efficiently store identity information like birth and death dates, marital status or property transfers, etc., on encrypted identity wallets, enabling security, control, and streamlining attestations.
Government can store land, property, or vehicle transaction record on a distributed ledger, making it easier to verify ownership and transfers.
Blockchain-based smart contracts can improve contract creation and execution, as demonstrated by the Swedish land registry’s use of blockchain for land-title transfers. The disintermediation and removal of notarization have reduced transaction time by more than 90 percent.
Figure 4: The proposed consortium blockchain e-government system
Cybersecurity
Blockchain also finds its use in enhancing cybersecurity and protecting against data breaches. An estimate in 2020 suggested that we generate 1.7MB of data per person per second. That makes a lot of information per day that is vulnerable to human error, phishing, hacking, or malware attacks.
Blockchain improves security by distributing data between several nodes instead of storing it in a central server. So to hack a system, hackers would have to take control of the maximum number of network nodes instead of a single server, making it highly difficult.
Blockchain systems can cross-reference data automatically and notice any misrepresented information. Blockchain records are encrypted, ensuring tamper-proof transactions.
Media
The media industry has also adopted blockchain technology because of benefits like efficiency, transparency, and cost efficiency. Blockchain provides greater security for Intellectual Property (IP) and prevents copyright infringement. The global market of blockchain in media and entertainment is estimated to reach $1 billion in 2023.
Blockchain disrupts the industry structure by allowing copyright owners to bypass content aggregators, platform providers, and royalty collection associations to a large extent. This technology revolutionizes pricing, advertising, revenue sharing, and royalty payment processes.
Blockchain improves the monetization of content sharing between consumers (C2C) and peer-to-peer (P2P) interactions by making them transparent and trackable. Real-time billing and reduced complexity of rights management are among the benefits.
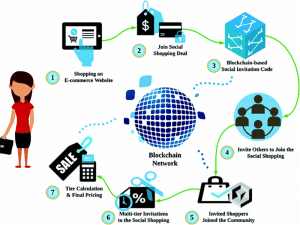
Figure 5
Agriculture
Blockchain technology is also highly significant for the agriculture industry as it improves efficiency, trust, and transparency. It can track and record information about plants, seed quality, crop growth, and the entire supply chain, enhancing transparency and eliminating concerns related to illegal operations and unethical practices. Blockchain also aids in tracking contamination and facilitating recalls.
The use of blockchain in agriculture can be categorized into four broad categories: intelligent farming, food supply chain, insurance for agriculture, and agricultural product transactions. Intelligent farming involves leveraging technologies such as IoT, sensors, and machine learning to enhance the efficiency and reliability of the farming process. Blockchain provides a decentralized and secure system for managing smart technology, preventing data manipulation and cyber-attacks.
In the food supply chain, blockchain improves transparency, traceability, and trust between producers and consumers. It allows specific product information to be stored on the blockchain, providing consumers with trustworthy information about food production. This technology empowers consumers to make informed purchasing decisions and rewards farmers and producers who implement good farming techniques.
Blockchain can also revolutionize agricultural insurance by enabling index-based insurance, which triggers reimbursement based on quantifiable indicators rather than loss assessment. This improves the accuracy and efficiency of insurance processes, benefiting both farmers and insurance companies.
Infrastructure and Energy
Blockchain technology plays a significant role in the infrastructure and energy sector by improving efficiency, transparency, and security as in other industries. The implementation of blockchain can lead to a reduction in costs associated with financial intermediaries and markets, allowing for more intense competition and lower entry barriers for new players. This shift towards a more competitive structure in the financial sector can benefit consumers and businesses alike.
In the energy sector, blockchain offers solutions to challenges related to sustainability, supply chain management, and transaction efficiency. By eliminating the need for centralized intermediaries, blockchain enables secure and automated energy transactions between producers, suppliers, and consumers. It also facilitates the use and transfer of electricity on a local scale, promoting the adoption of smart grids and meters.
Information and Communication
Blockchain technology is making significant strides in the information and communication sector, revolutionizing various areas such as telecommunications, messaging apps, publishing, education and academia, libraries, entertainment, social media content, sports management, gambling, art, and photography.
In the field of telecommunications, blockchain technology presents a unique opportunity for identity management services. With its ability to securely store and verify data, blockchain allows for tamper-proof identity verification in the telecom sector. Customers can have greater control over sharing their data with specific companies, ensuring privacy and security. Additionally, blockchain facilitates transparent and efficient contract management, making it easier for stakeholders in the telecom industry to collaborate on infrastructure projects and implement cost-saving sharing models.
Messaging apps are integrating blockchain capabilities to enhance user security and privacy. Platforms like Status and Signal provide encrypted messaging services that prioritize user privacy, while blockchain technology ensures the authenticity and integrity of news content, combating misinformation and manipulation.
Publishing is being disrupted by blockchain through platforms like Bookchain and Publica, which enable authors and publishers to bypass traditional intermediaries, directly transact with readers, and protect intellectual property rights. Blockchain also secures news photos and records their metadata, preventing manipulation or sharing out of context.
Education and academia benefit from blockchain’s ability to secure and share student records. Platforms like Sony Global Education and Learning Machine offer blockchain-based solutions for verifying academic credentials and streamlining verification processes. Libraries are exploring blockchain’s potential to enhance metadata archives, support community-based collections, and manage digital rights effectively.
Conclusion
In conclusion, blockchain technology has emerged as a game-changer across various industries, offering solutions to longstanding challenges and transforming traditional processes. Its applications extend beyond the industries mentioned in this article, with healthcare, finance, supply chain management, government, cybersecurity, media, agriculture, infrastructure, energy, and information and communication sectors all benefiting from blockchain’s capabilities. From secure identity management and efficient contract management to enhanced transparency, traceability, and automation, blockchain has the potential to revolutionize the way industries operate and interact. As blockchain continues to evolve and gain adoption, we can expect further advancements and innovations in diverse fields, leading to more secure, efficient, and transparent systems.
Blockchain technology is being utilized in many other industries beyond those discussed in this article, such as real estate, insurance, logistics, retail, voting systems, charity, music, gaming, and more are embracing blockchain to enhance security, streamline processes, and create decentralized ecosystems.
. . .
To learn more about variance and bias, click here and read our another article.
Source:
Blockchain applications in health care for COVID-19 and beyond: a systematic review, Ng, Wei Yan et al.,The Lancet Digital Health, Volume 3, Issue 12, e819 – e829
https://www.thelancet.com/journals/landig/article/PIIS2589-7500%2821%2900210-7/fulltext#articleInformation
Figure 2: https://mahanakornpartners.com/revolutionizing-trade-finance-with-blockchain-technology/
Figure 3: Lumineau, Fabrice & Wang, Wenqian & Schilke, Oliver. (2020). Blockchain Governance—A New Way of Organizing Collaborations?. Organization Science. 10.1287/orsc.2020.1379.
Figure 4: Elisa, N & Yang, Longzhi & Li, Honglei & Chao, Fei & Naik, N & Nnko, Noe & Yang, Li & Chao,. (2019). Consortium Blockchain for Security and Privacy-Preserving in E-government Systems.
Figure 5: https://www.europeanbusinessreview.com/are-blockchain-based-digital-networks-the-future-of-social-media/



