According to the Stackoverflow community survey in 2022, the respondents were asked which database environments they have done extensive development work in over the past year, and which they want to work in over the next year. Even though below answers have a mingle of relational database management systems with the others, in this article, we will compare the top three RDBMS: Microsoft SQL, MySQL, and PostgreSQL.

Microsoft SQL
Out of all three, MS SQL is the only one that is not open source. MS SQL is a proprietary RDBMS developed by Microsoft. It is most widely used in enterprise environments and is known for its support for high-availability and scalability features. MS SQL has several built-in business intelligence, data warehousing and data mining features. It is a good choice for enterprise environments and for applications that require high levels of availability and scalability. MS SQL also has built-in support for disaster recovery, which can be important in data science projects that require 24×7 uptime. MS SQL can be easily integrated with other Microsoft technologies, such as Azure, Power BI, and Visual Studio, which can be useful for data science projects that use these tools.

PostgreSQL
PostgreSQL is an open-source RDBMS with a strong support for advanced data types, such as arrays and hstore (a key-value store). It also has built-in support for full-text search, and is often used for advanced analytics and business intelligence workloads.
PostgreSQL is highly extensible and allows for the creation of custom functions, operators, and data types, making it a good choice for customizing the database to specific requirements.
PostgreSQL also supports the ACID properties, which ensures the reliability of the data and the consistency of the database. PostgreSQL has connectors to many open-source ETL tools such as Talend, Apache Nifi, and Apache Airflow, which can be useful in data science projects that require ETL functionalities. PostgreSQL uses Multi-Version Concurrency Control (MVCC), which allows multiple users to access the same data simultaneously without blocking each other, while MS SQL uses a different concurrency control model that can result in more locking and blocking.
PostgreSQL supports for triggers and rules, which allows for automatic updates, data validation, and auditing of data changes in the database.

MySQL
MySQL is another open-source RDBMS, which is widely used for web-based applications and is known for its reliability and ease of use. It is also one of the most popular databases for use with the LAMP (Linux, Apache, MySQL, and PHP) stack. MySQL is a good choice for small to medium-sized web-based applications because it is easy to set up and use, and there is a large community of developers who can provide support and tutorials. In data science, MySQL may not be the first choice due to its limited support for advanced data types and analytics features compared to other RDBMS such as PostgreSQL and MS SQL. However, MySQL may still be a viable option for certain use cases. MySQL is known for its ease of use, making it a good choice for data science projects that require a quick and simple setup.
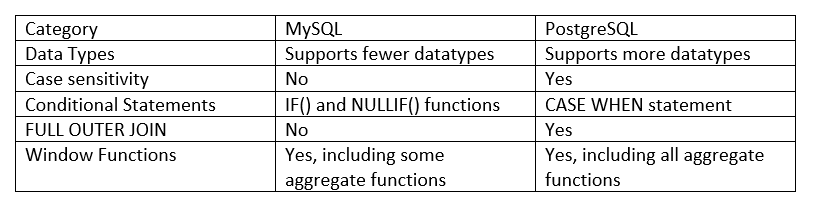
Even though it is not our intention to extensively compare PostgreSQL and MySQL, below is a sample table for a few categories. Both RDBMS are open source. For that reason, it is unavoidable to have both dialects in data science.
When working with data, one of the decision makers is the availability of the data types in the RBDMS especially if your work requires more than the basics. In that sense, PostgreSQL supports more datatypes than MySQL.
Another difference is the window functions. Even though both offers the same window functions, PostgreSQL offers much more aggregate functions to be used as window functions. PostgreSQL simply offers more possibilities when it comes to data analysis. Below table shows some of the differences in some categories between the two RDBMS.

Conclusion
In conclusion, PostgreSQL, MySQL, and MS SQL are all popular RDBMS, and each one has its own strengths and use cases. PostgreSQL is best suited for advanced analytics and business intelligence workloads, MySQL is best for small to medium-sized web-based applications, and MS SQL is best for enterprise environments and applications that require high levels of availability and scalability. Ultimately, the choice of which RDBMS to use will depend on the specific requirements of your project.
To learn more about variance and bias, click here and read our another article.